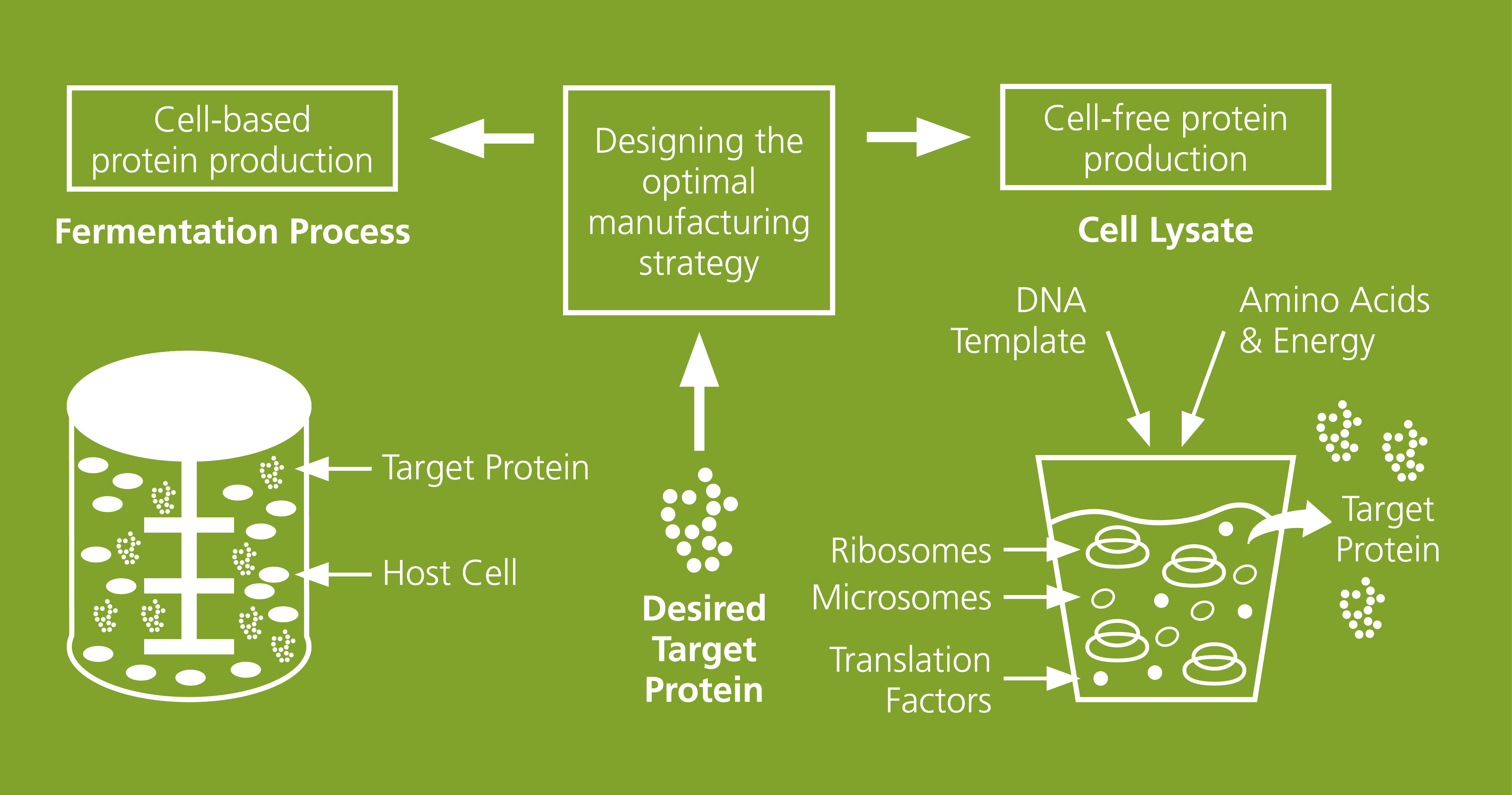
The research field of cell-free protein synthesis deals with the synthesis of recombinant proteins in various cell-free systems. In order to analyze proteins, they must first be made available in a functionally active form. The expression of proteins in living cells, i.e. in vivo, is widely used, but does not always lead to the desired goal, since not every protein can be synthesized satisfactorily in cell cultures. An efficient alternative to the expression of proteins in living cells is therefore cell-free protein synthesis. Here, the cell's constituents are used to produce a specific target protein in a rapid and cost-effective manner. The use of eukaryotic cell lysates offers the particular advantage that they allow the synthesis of proteins with post-translational modifications (PTMs). A particular focus is on the characterization, modification and functional investigation of cell-free produced antibody formats and membrane proteins. Cell-free systems are used in time-saving, highly parallelized procedures to synthesize antibodies and membrane proteins and to directly perform functional analysis.
Protein Synthesis
The production of recombinant proteins is one of the core issues of today's biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry. Each protein requires individually adapted production processes in order to ensure not only the highest quality but also a maximum yield. Our institute has many years of expertise in the production of recombinant proteins and the associated process optimization. In addition to conventional, cell-based production, our specialization lies primarily in cell-free protein synthesis. This method not only enables a faster production time and makes the synthesis process economical, but also makes the process more flexible and easier to control. In addition, this technology enables the production of proteins that are otherwise difficult to produce, such as membrane proteins or proteins with cytotoxic effects.
Range of services:
- »in vivo« versus »in vitro« (cell-based versus cell-free): comparisons of gene sequences, promoter sequences, signal peptides and purity markers for the improvement and acceleration of industrial production pipelines
Cell-free synthesis
- Cell-free synthesis of membrane proteins and toxic proteins
- Nanodisks for embedding membrane proteins
- Fast and functional analysis of ion channels, transporter proteins and pore-forming, toxic proteins directly after synthesis by electrophysiological methods in planar double lipid layers
- Tailor-made cell-free systems for customer-specific applications
- Prokaryotic cell-free systems based on E.coli lysates
- Eukaryotic cell-free systems based on CHO, Sf21 and K562 cell lysates
- Upscaling of cell-free systems for the production and purification of medically relevant proteins
- Development of new HTS methods and HTS-compatible systems for screening applications
- Customization of cell lines for customized cell-free systems
Applications

Tabbed contents
Methods
- Production, optimization and cloning of "ready-to-express" DNA templates for cell-free protein synthesis.
- RNA synthesis (transcription, analysis and purification of mRNA)
- Cell-free synthesis and characterization of recombinant antibody formats
- Synthesis of recombinant antibody formats based on linear or circular DNA templates in eukaryotic in vitro transcription-translation systems
- Parallel production of antibody formats in different reaction modes, e.g. batch and dialysis mode or coupled (transcription and translation in one reaction system) and uncoupled (transcription and translation in separate reactions)
- Determination of synthesis yield by (14C)-protein labeling and TCA precipitation.
- Characterization of protein expression by gel electrophoresis, autoradiography and quantitative imaging in a phosphorimager
- Protein analysis by fluorescence microscopy and western blotting
- Directed protein evolution by mutagenesis and activity screening
- Cotranslational labeling of antibody fragments, e.g. with fluorescent dyes
- Functional studies on cell-free produced antibody fragments e.g. by ELISA
- Optimization of in vitro translation systems for the synthesis of disulfide-bridged proteins
Equipment
Cell culture laboratories of safety class S1
- 5 L fermenter (Sartorius Biostat B DCU-II Advanced Additive Flow System; 2x 5 l vessels, upgradeable with up to 6 vessels between 1 and 10 l)
- 30 L fermenter (Sartorius Biostat D DCU)
- Confocal laser scanning microscope (Zeiss CLSM 510)
- Automated cell assay and screening unit (PerkinElmer; CellLuxCellularFluorescence Workstation)
Isotope laboratory
- Protein labeling (handling of 14C, 32P, 35S)
- Extraction system for separation of 14C-labeled protein precipitates (TCA precipitation)
- Scintillation counter (Beckmann LS 6500 Multi Purpose Scintillation Counter)
- Gel drying system for autoradiograms (Unigeldryer 3545)
- Typhoon Trio+ variable-mode imager (radioactivity, fluorescence and chemiluminescence with extended 10 µm pixel scan)
Safety class S1 laboratories for molecular biology work
- Multimode Reader Berthold LB 941 vi-S TriStar (flash, glow and color luminescence, absorption, fluorescence, FRET, BRET)
- Sirius single tube luminometer (Titertek Berthold)
- Spectrophotometer for UV/Vis (Nanodrop ND-2000c)
- Bioreactors for cell-free protein synthesis in batch and dialysis scale
Mass spectrometry in safety class S1 laboratories
- Mass spectrometer Q-TOF MaxIs Impact (Bruker Daltonics) with exchangeable ion sources (offline nanoESI source, conventional ESI source, captive spray for nano-LC coupling)
- Ultra-sensitive ion trap AmaZon Speed ETD (Bruker Daltonics) with exchangeable ion sources (conventional ESI source, captive spray for nano-LC coupling)
- UHPLC chromatography systems, Ultimate 3000 nanoRSLC system (Dionex)
Analysis of membrane proteins in laboratories of safety class S1
- Patch-Clamp System "Port-A-Patch" and Orbit 16 of the company Nanion
- Particle analysis by means of "Zetasizer Nano ZS" of the company Malvern
Publications & Patents
- Ullrich, J.; Göhmann, P. J.; Zemella, A.; Kubick, S. (2022) Oligomerization of the heteromeric γ-aminobutyric acid receptor GABAB in a eukaryotic cell-free system. Scientific reports. 10.1038/s41598-022-24885-0.
- Schloßhauer, J. L.; Cavak, N.; Zemella, A.; Thoring, L.; Kubick, S. (2022) Cell Engineering and Cultivation of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for the Development of Orthogonal Eukaryotic Cell-free Translation Systems. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 10.3389/fmolb.2022.832379.
- Ramm, F.; Jack, L.; Kaser, D.; Schloßhauer, J. L.; Zemella, A.; Kubick, S. (2022) Cell-Free Systems Enable the Production of AB5 Toxins for Diagnostic Applications. Toxins. 10.3390/toxins14040233.
- Ramm, F.; Dondapati, S. K.; Trinh, H. A.; Wenzel, D.; Walter, R. M.; Zemella, A.; Kubick, S. (2022) The Potential of Eukaryotic Cell-Free Systems as a Rapid Response to Novel Zoonotic Pathogens: Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Proteins. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 10.3389/fbioe.2022.896751.
- Knauer, J. F.; Liers, C.; Hahn, S.; Wuestenhagen, D. A.; Zemella, A.; Kellner, H.; Haueis, L.; Hofrichter, M.; Kubick, S. (2022) Cell-free production of the bifunctional glycoside hydrolase GH78 from Xylaria polymorpha. Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2022.110110.
- Walter, R. M.; Zemella, A.; Schramm, M.; Kiebist, J.; Kubick, S. (2022) Vesicle-based cell-free synthesis of short and long unspecific peroxygenases. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 10.3389/fbioe.2022.964396.
- Haueis, L.; Stech, M.; Kubick, S. (2022) A Cell-free Expression Pipeline for the Generation and Functional Characterization of Nanobodies. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 10.3389/fbioe.2022.896763.
- Krebs, S. K.; Stech, M.; Jorde, F.; Rakotoarinoro, N.; Ramm, F.; Marinoff, S.; Bahrke, S.; Danielczyk, A.; Wüstenhagen, D. A.; Kubick, S. (2022) Synthesis of an Anti-CD7 Recombinant Immunotoxin Based on PE24 in CHO and E. coli Cell-Free Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 10.3390/ijms232213697.
- Krebs, S. K.; Rakotoarinoro, N.; Stech, M.; Zemella, A.; Kubick, S. (2022) A CHO-Based Cell-Free Dual Fluorescence Reporter System for the Straightforward Assessment of Amber Suppression and scFv Functionality. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.873906.
- Ramm, F.; Stech, M.; Zemella, A.; Frentzel, H.; Kubick, S. (2021) The Pore-Forming Hemolysin BL Enterotoxin from Bacillus cereus: Subunit Interactions in Cell-Free Systems. Toxins. 10.3390/toxins13110807.
- Stech, M.; Rakotoarinoro, N.; Teichmann, T.; Zemella, A.; Thoring, L.; Kubick, S. (2021) Synthesis of Fluorescently Labeled Antibodies Using Non-Canonical Amino Acids in Eukaryotic Cell-Free Systems. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.). 10.1007/978-1-0716-1406-8_9.
- Dhandapani, P.; Dondapati, S. K.; Zemella, A.; Bräuer, D.; Wüstenhagen, D. A.; Mergler, S.; Kubick, S. (2021) Targeted esterase-induced dye (TED) loading supports direct calcium imaging in eukaryotic cell-free systems. RSC advances. 10.1039/d0ra08397f.
- WÜSTENHAGEN, D.A., LUKAS, P., Müller, C., Aubele, S.A., Hildebrandt, J-P., KUBICK, S.: „Cell-free Synthesis of the hirudin variant 1 of the blood-sucking leech Hirudo medicinalis” Sci Rep 10, 19818 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76715-w
- Dondapati, S.K., STECH, M., M., ZEMELLA, A., KUBICK, S.: Cell‑Free Protein Synthesis: A Promising Option for Future Drug Development. BioDrugs (2020), https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-020-00417-y
- RAMM, F., DONDAPATI, S.K., THORING L., ZEMELLA A., WÜSTENHAGEN, D.A., FRENTZEL, H., STECH M., KUBICK, S.: “Mammalian cell-free protein expression promotes the functional characterization of the tripartite non-hemolytic enterotoxin from Bacillus cereus”. Sci Rep. 10, 2887 (2020).
- ZAITSEVA, E., DONDAPATI, S., SCHLOßHAUER, J., ZEMELLA, A., DHANDAPANI, P., KUBICK, S., BAAKEN, G.: „Functional Characerization of Ion Channels Expressed in Eukaryotic Cell-free Systems using Lipid Bilayer Arrays”. Biophysical Journal (2020), Volume 118, Issue 3, Supplement 1, 586A.Dondapati, S.K., STECH, M., M., ZEMELLA, A., KUBICK, S.: Cell‑Free Protein Synthesis: A Promising Option for Future Drug Development. BioDrugs (2020), https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-020-00417-y
- RAMM, F., DONDAPATI, S.K., THORING L., ZEMELLA A., WÜSTENHAGEN, D.A., FRENTZEL, H., STECH M., KUBICK, S.: “Mammalian cell-free protein expression promotes the functional characterization of the tripartite non-hemolytic enterotoxin from Bacillus cereus”. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:2887.
- Jérôme V, Thoring L, Salzig D, Kubick S, Freitag R. Comparison of cell-based versus cell-free mammalian systems for the production of a recombinant human bone morphogenic growth factor. Engineering in Life Sciences 2017 Aug 7. doi:10.1002/elsc.201700005
- Zemella A, Grossmann S, Sachse R, Sonnabend A, Schaefer M, Kubick S. Qualifying a eukaryotic cell-free system for fluorescence based GPCR analyses. Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 16;7(1):3740. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-03955-8. Artikel
- Georgi V, Georgi L, Blechert M, Bergmeister M, Zwanzig M, Wüstenhagen DA, Bier FF, Junga E, Kubick S. On-chip automation of cell-free protein synthesis: new opportunities due to a novel reaction mode. Lab Chip. 2016 Jan 5;16(2):269-81. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1039/c5lc00700c. Artikel
- Quast RB, Ballion B, Stech M, Sonnabend A, Varga BR, Wüstenhagen DA, Kele P, Schiller SM, Kubick S. Cell-free synthesis of functional human epidermal growth factor receptor: Investigation of ligand-independent dimerization in Sf21 microsomal membranes using non-canonical amino acids. Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 27;6:34048. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep34048 Artikel
- Quast RB, Sonnabend A, Stech M, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S. High-yield cell-free synthesis of human EGFR by IRES-mediated protein translation in a continuous exchange cell-free reaction format. Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 26;6:30399. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep30399 Artikel
- Thoring L, Wüstenhagen DA, Borowiak M, Stech M, Sonnabend A, Kubick S. Cell-Free Systems Based on CHO Cell Lysates: Optimization Strategies, Synthesis of »Difficult-to-Express« Proteins and Future Perspectives. PLoS One. 2016 Sep 29;11(9):e0163670. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163670 Artikel
- Zemella A, Thoring L, Hoffmeister C, Kubick S. Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Pros and Cons of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Systems. Chembiochem. 2015 Oct 19. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201500340. [Epub ahead of print] Artikel
- Quast RB, Mrusek D, Hoffmeister C, Sonnabend A, Kubick S. Cotranslational incorporation of non-standard amino acids using cell-free protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 2015 Jul 8;589(15):1703-12. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.041. Epub 2015 May 1. Artikel
- Bechlars S, Jäckel C, Diescher S, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S, Dieckmann R, Strauch E. Characterization of trh2 Harbouring Vibrio parahaemolyticus Strains Isolated in Germany. PLOS ONE | DOI dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118559. Artikel
- Quast RB, Kortt O, Henkel J, Srujan KD, Wüstenhagen DA, Stech M, Kubick S. Automated production of functional membrane proteins usingeukaryotic cell-free translation systems. Journal of Biotechnology 203 (2015) 45–53. Artikel
- Brödel AK, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S. Cell-Free Protein Synthesis Systems Derived from Cultured Mammalian Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1261:129-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2230-7_7.
- Stech M, Kubick K. Cell-Free Synthesis Meets Antibody Production: A Review. Antibodies 2015, 4, 12-33; DOI dx.doi.org/10.3390/antib4010012.
- Dondapati SK, Kreir M, Quast RB, Wüstenhagen DA, Brüggemann A, Fertig N, Kubick S. Membrane assembly of the functional KcsA potassium channel in a vesicle-based eukaryotic cell-free translation system. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Sep 15;59:174-83.
- Sachse R, Dondapati SK, Fenz SF, Schmidt T, Kubick S. Membrane protein synthesis in cell-free systems: from bio-mimetic systems to bio-membranes. FEBS Letter. 2014 Aug 25;588(17):2774-81. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.06.007
- Stech M, Hust M, Schulze C, Dübel S, Kubick S. Cell-free eukaryotic systems for the production, engineering, and modification of scFv antibody fragments. Engineering in Life Sciences. 2014;14(4):387–398. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201400036.
- Stech M, Quast RB, Sachse R, Schulze C, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S. A continuous-exchange cell-free protein synthesis system based on extracts from cultured insect cells. PLoS One 9 (2014) e96635.
- Scheller FW, Yarman A, Bachmann T, Hirsch T, Kubick S, Renneberg R, Schumacher S, Wollenberger U, Teller C, Bier FF. Future of biosensors: a personal view. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2014;140:1-28.
- Stech M, Brödel AK, Quast RB, Sachse R, Kubick S. Cell-free systems: functional modules for synthetic and chemical biology. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, Springer Berlin Heidelberg (2013) 67-102.
- Quast RB, Claussnitzer I, Merk H, Kubick S, Gerrits M. Synthesis and site-directed fluorescence labeling of azido proteins using eukaryotic cell-free orthogonal translation systems. Anal Biochem. 2014 Apr 15;451:4-9.
- Fenz SF, Sachse R, Schmidt T, Kubick S. Cell-free synthesis of membrane proteins: tailored cell models out of microsomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2014 May;1838(5):1382-8. DOI dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.12.009.
- Sachse R, Wüstenhagen D, Samal?kova M, Gerrits M, Bier FF, Kubick S. Synthesis of membrane proteins in eukaryotic cell-free systems. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, No. 1, 39–48.
- Bechlars S, Wüstenhagen DA, Drägert K, Dieckmann R, Strauch E, Kubick S. Cell-free synthesis of functional thermostable direct hemolysins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Toxicon. 2013 Dec 15;76:132-42.
- Brödel AK, Sonnabend A, Kubick S. Cell-free protein expression based on extracts from CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2014 Jan;111(1):25-36.
- Brödel AK, Sonnabend A, Roberts L, Stech M, Wüstenhagen DA, Kubick S. IRES-Mediated translation of membrane proteins and glycoproteins in eukaryotic cell-free systems. PLoS One 8 (2013) e82234.
- Brödel AK, Raymond JA, Duman JG, Bier FF, Kubick S. Functional evaluation of candidate ice structuring proteins using cell-free expression systems. J Biotechnol. 2013 Feb 10;163(3):301-10.
- Stech M, Merk H, Schenk JA, Stöcklein W, Wüstenhagen DA, Micheel B, Duschl C, Bier FF, Kubick S. Production of functional antibody fragments in a vesicle-based eukaryotic cell-free translation system. J Biotechnol. 164 (2012) 220-231.
- Zampatis DE, Rutz C, Furkert J, Schmidt A, Wüstenhagen D, Kubick S, Tsopanoglou NE, Schülein R. The protease-activated receptor 1 possesses a functional and cleavable signal peptide which is necessary for receptor expression. FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 30;586(16):2351-9.
Patents
STECH, Marlitt; HANACK, Katja; MESSERSCHMIDT, Katrin; KUBICK, Stefan: METHOD FOR PRODUCING POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES USING AN ANTIGENIC COMPOSITION COMPRISING PROTEIN-CONTAINING MEMBRANE VESICLES. PCT/EP2014/002592
STECH, MARLITT; QUAST, ROBERT; WUESTENHAGEN, DOREEN; KUBICK, STEFAN: Verfahren und vorrichtung zur zellfreien proteinsynthese in gegenwart eines caspase-inhibitors. PCT/EP2014/002520
 Fraunhofer Institute for Cell Therapy and Immunology, Branch Bioanalytics and Bioprocesses IZI-BB
Fraunhofer Institute for Cell Therapy and Immunology, Branch Bioanalytics and Bioprocesses IZI-BB